Step-by-Step Guide to Plant Formation: Learn How Plants Grow
The Miracle of Plant Formation
Plants are the backbone of life on Earth, providing oxygen, food, and countless other resources. Understanding how they form is not just a scientific pursuit – it’s a window into the very foundations of life itself. Whether you’re a budding gardener, a curious student, or simply someone who marvels at the natural world, this guide will illuminate the incredible process of plant formation.
Seeds:
The Structure of Seeds
Every plant’s journey begins with a seed. These tiny powerhouses contain everything needed to kickstart a new life. Let’s break down the key components:
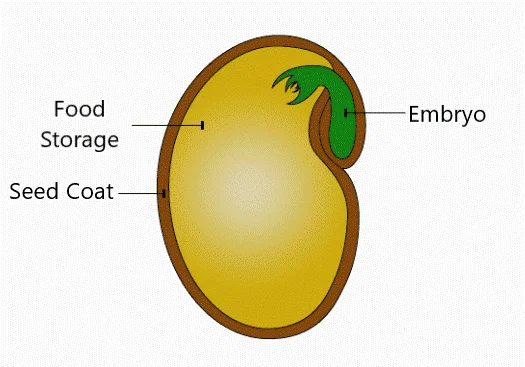
- Embryo: The baby plant, waiting to emerge
- Endosperm: Nutrient storage to fuel initial growth
- Seed coat: Protective outer layer
Dormancy and Germination
Seeds can remain dormant for years, patiently waiting for the right conditions. When moisture, temperature, and light align perfectly, the magic of germination begins. I’ve seen seeds sprout after decades of dormancy – a true testament to their resilience!
Roots: Anchoring and Nourishing
Primary Root Development
As the seed germinates, the first structure to emerge is usually the primary root, or radicle. This root anchors the young plant and begins absorbing water and nutrients.
Root System Expansion
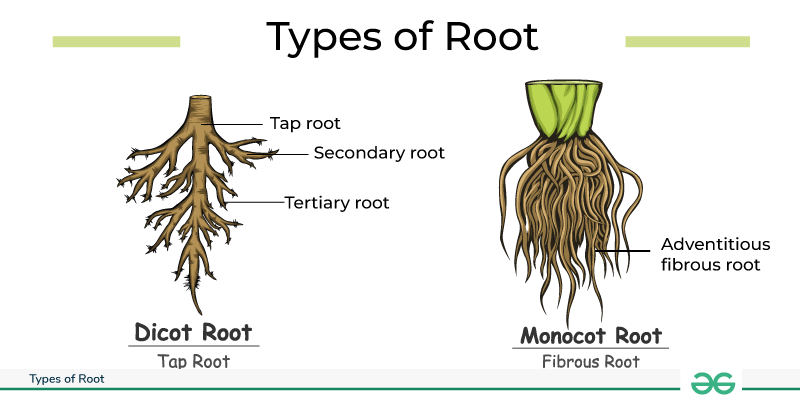
Over time, secondary roots branch out, creating a complex network. Some plants develop:
- Taproots: Deep, central roots (like carrots)
- Fibrous roots: Widespread, shallow systems (like grass)
Shoots: Reaching for the Sky
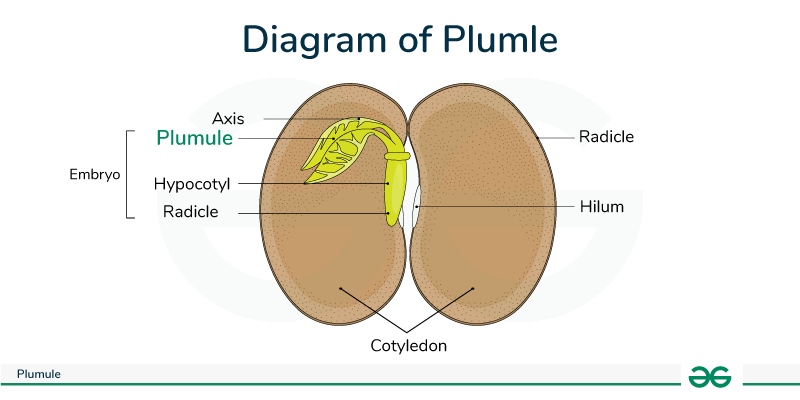
The Plumule Emerges
Following the root, the shoot (plumule) pushes upward, seeking light. This delicate structure will become the plant’s stem and first leaves.
Leaf Development
Leaves are the plant’s solar panels and food factories. They start as tiny buds and unfurl into intricate structures designed to capture sunlight and facilitate photosynthesis.
Vascular System: The Plant’s Lifeline
Xylem and Phloem
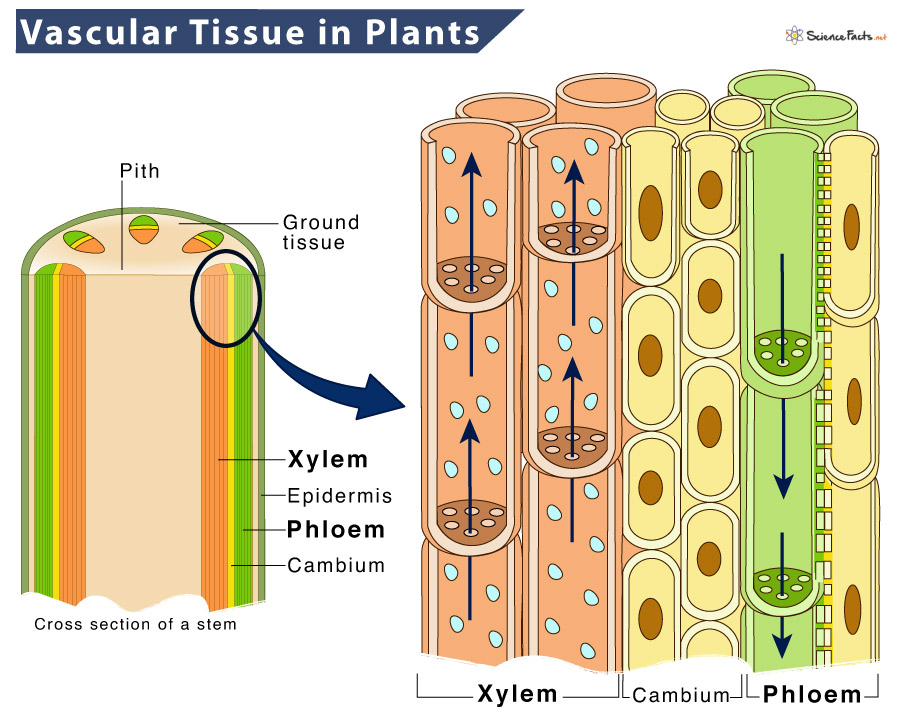
As the plant grows, it develops a sophisticated transport system:
- Xylem: Carries water and minerals upward
- Phloem: Distributes sugars and other nutrients throughout the plant
This vascular system is crucial for sustained growth and development.
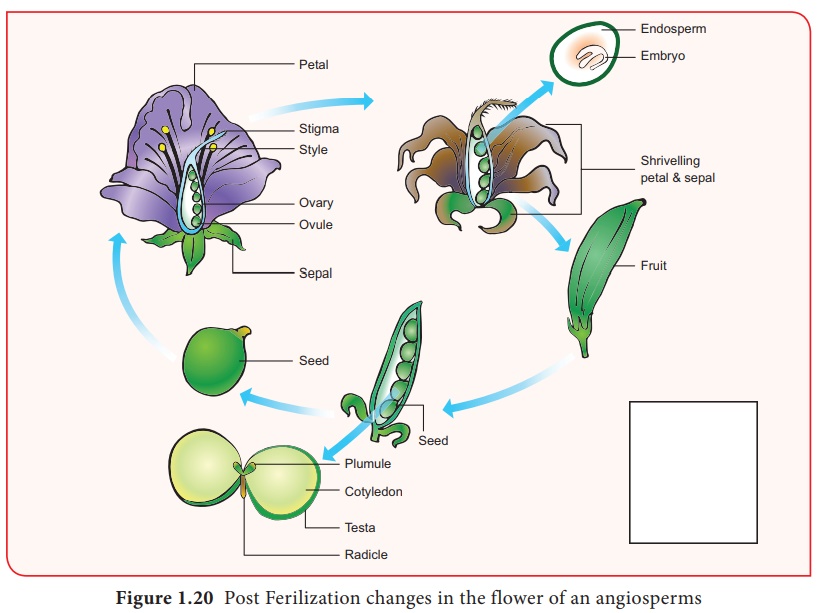
Flowering: Nature’s Grand Finale
Flower Formation
For many plants, the ultimate goal is reproduction. Flowers are the reproductive organs, with intricate structures designed to attract pollinators and facilitate genetic exchange.
From Flower to Fruit
After pollination, flowers transform into fruits, protecting the next generation of seeds. This completes the cycle of plant formation, ready to begin anew.
The Science Behind Plant Formation
Cellular Division and Differentiation
At the heart of plant formation is the process of cell division and specialization. Meristematic tissues at the tips of roots and shoots contain stem cells that can become any plant cell type.
Hormonal Regulation
Plant hormones, or phytohormones, orchestrate the entire process of plant formation. Key players include:
- Auxins: Promote cell elongation and root formation
- Cytokinins: Stimulate cell division and shoot growth
- Gibberellins: Encourage stem elongation and seed germination
Environmental Influences
Plants are masters of adaptation, constantly responding to their environment. Factors like light, gravity, and touch all influence how a plant forms and grows.
Practical Applications of Plant Formation Knowledge
Understanding plant formation has numerous real-world applications:
- Agriculture: Optimizing crop yields and developing resilient varieties
- Conservation: Protecting and propagating endangered plant species
- Medicine: Discovering new plant-based treatments
- Space exploration: Developing sustainable food sources for long-term missions
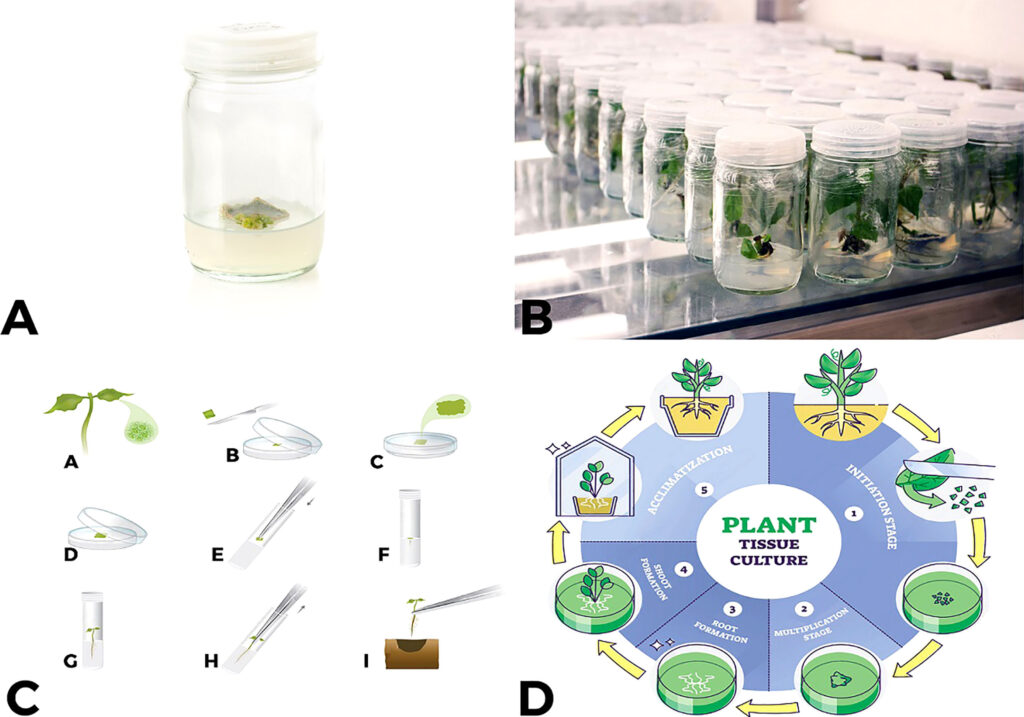
Cutting-Edge Research in Plant Formation
Scientists are continually uncovering new insights into plant formation. Some exciting areas of current research include:
- Genetic engineering to enhance desirable traits
- Studying plant adaptations to climate change
- Exploring the potential of vertical farming and urban agriculture
Tips for Nurturing Healthy Plant Formation
As someone who’s grown countless plants both in the lab and at home, here are my top tips for supporting healthy plant formation:
- Start with high-quality seeds or seedlings
- Provide consistent moisture during germination
- Ensure adequate light for strong stem and leaf development
- Use well-draining soil to promote healthy root growth
- Fertilize appropriately to support overall plant health
Common Challenges in Plant Formation
Even with the best care, plants can face obstacles during their development. Here are some issues I’ve encountered and how to address them:
- Damping off: A fungal disease that affects seedlings. Prevent by using sterile soil and avoiding overwatering.
- Leggy seedlings: Caused by insufficient light. Provide more light or use grow lamps.
- Root-bound plants: When roots outgrow their container. Transplant to a larger pot or in-ground.
Read also: https://plantgrowup.com/how-to-improve-plant-growth-expert-tips-for-thriving-gardens/
Conclusion: The Wonder of Plant Formation
Understanding plant formation isn’t just an academic exercise – it’s key to addressing some of our most pressing global challenges, from food security to climate change mitigation. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of how plants grow and develop, we open up new possibilities for sustainable agriculture, environmental conservation, and even space exploration.
Whether you’re nurturing a windowsill herb garden or studying plant biology in a state-of-the-art laboratory, I hope this guide has deepened your appreciation for the incredible journey of plant formation. The next time you see a seedling pushing through the soil or a flower blooming in your garden, take a moment to marvel at the complex processes at work.
People also ask:
How long does it take for a seed to germinate?
Germination time varies widely depending on the plant species and environmental conditions. Some seeds, like radishes, can sprout in as little as 3-5 days. Others, like certain tree species, may take months or even years to germinate.
Can plants grow without soil?
Yes! Hydroponic and aeroponic systems allow plants to grow using nutrient-rich water solutions instead of soil. These methods are becoming increasingly popular in urban farming and space exploration research.
How do plants know which way is up?
Plants use a process called gravitropism to sense and respond to gravity. Special cells in the root tips contain dense starch grains that settle to the bottom of the cell, indicating the direction of gravity and guiding root growth downward.
Why do some plants flower and others don’t?
Flowering is a reproductive strategy used by angiosperms (flowering plants). Non-flowering plants, like ferns and mosses, reproduce through spores. Some plants require specific environmental cues, like day length or temperature changes, to initiate flowering.
Can plants communicate with each other?
While plants don’t “talk” in the way animals do, they can communicate through chemical signals. For example, when under attack by pests, some plants release volatile organic compounds that warn neighboring plants to activate their defenses.
Read also: https://plantgrowup.com/how-to-accelerate-plant-growth/